The previous post compared custom accommodative foot orthotics to custom function foot orthotics. Now, we proceed along the spectrum of treatment options to ankle foot orthotics. We will limit this discussion to custom AFO fabrication. The custom functional foot orthotic is designed to control abnormal motion of the foot, often compensatory in nature, improve biomechanics, and correct alignment during standing and gait. Usually made of rigid or semi-rigid materials (e.g., polypropylene, carbon fiber, hard plastics, dense foam materials). It is used for Overpronation or oversupination in all age groups and genders, flat feet or high arches with biomechanical issues, Sports and work performance enhancement Conditions like plantar fasciitis, tendinitis, patellofemoral pain syndrome, forefoot deformities such as Hallux Valgus and lesser metatarsal issues. Asymmetry issues, sports and work performance enhancement, conditions like plantar fasciitis, tendinitis, patellofemoral pain syndrome, forefoot deformities such as Hallux Valgus and lesser metatarsal issues. Asymmetry issues.
An AFO (Ankle-Foot Orthosis) is defined as a type of medical device designed to support the foot and ankle, typically for individuals with conditions that affect the lower extremities, such as foot drop, weakness, or paralysis. AFOs are often used to improve mobility, stabilize the ankle joint, and prevent abnormal movements of the foot and ankle during walking. The two primary types of AFOare the Richie Brace and Gauntlet AFO, however other type AFOs are available to KevinRoot Medical clients.
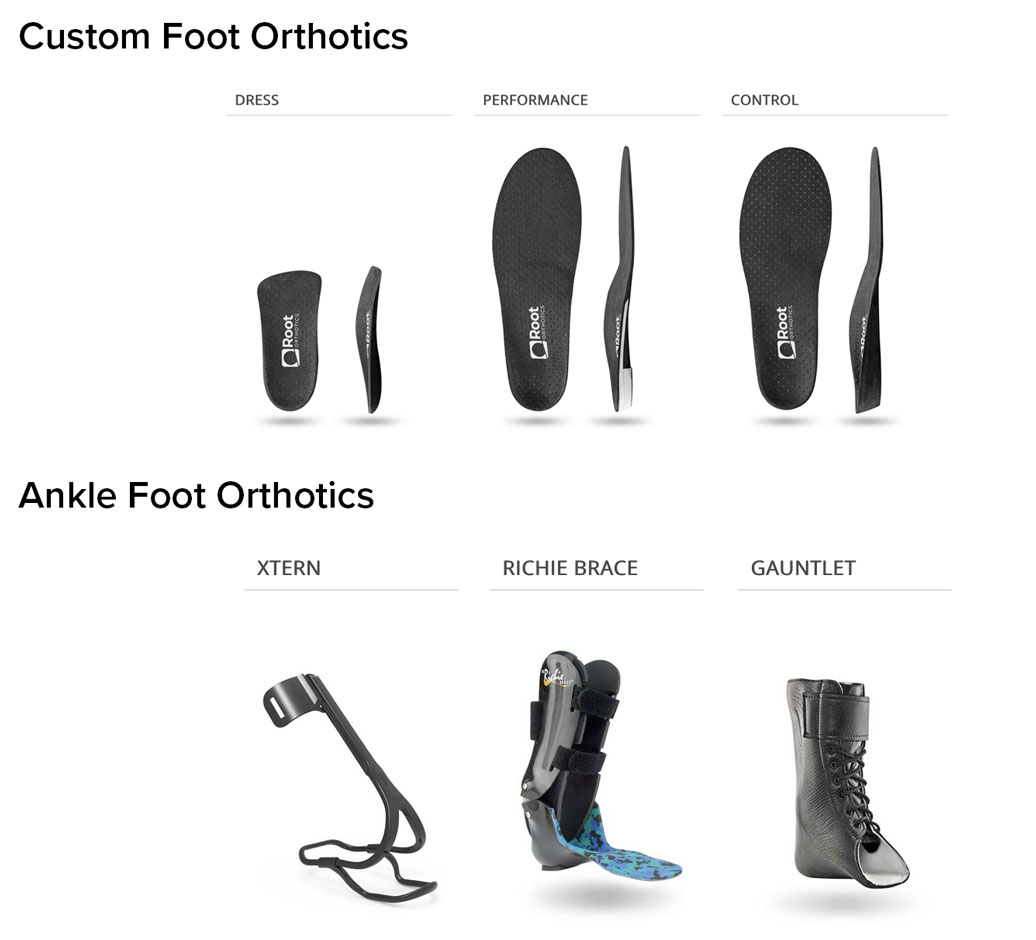
Types:
-
- Static AFO: This type is rigid and provides complete support and stability to the foot and ankle.
- Dynamic AFO: Offers some flexibility or movement to allow for more natural motion while still providing support.
- Articulating AFO: Includes hinges at the ankle joint, allowing for a limited range of movement (e.g., for walking).
- Prefabricated vs. Custom: AFOs can be custom-made to fit the individual's unique anatomy, or they can be prefabricated and adjusted for comfort and fit.
1. Primary Purpose
- Custom Foot Orthotic (CFO):
Designed to support, align, or redistribute pressure within the foot. Primarily addresses foot mechanics (arch collapse, forefoot deformity, heel alignment). - Custom Ankle Foot Orthotic (AFO):
Provides control, alignment, and support of both the ankle and foot. Extends above the ankle to influence gait, stability, and motion of the ankle joint in addition to the foot.
2. Conditions Addressed
- CFO:
- Plantar fasciitis
- Metatarsalgia
- Flatfoot (pes planus)
- High arches (pes cavus)
- Overpronation or oversupination
- Pressure offloading (e.g., diabetic ulcer prevention)
- AFO:
- Foot drop (neurologic weakness)
- Ankle instability (ligamentous or neuromuscular)
- Severe posterior tibial tendon dysfunction
- Charcot neuroarthropathy
- Stroke, MS, CP, or other neuromuscular disorders affecting ankle/foot control
- Severe arthritis or deformity affecting ankle/foot
3. Structure
- CFO:
- Typically a shoe insert that sits within the shoe, under the foot.
- Custom-molded from a cast, foam impression, or 3D scan of the foot.
- Made from materials like EVA, polypropylene, carbon fiber, or multilayer composites.
- AFO:
- A brace that encompasses the foot and extends upward around or behind the ankle/lower leg.
- Custom-molded from plaster or fiberglass cast or 3D imaging.
- May include rigid plastics, carbon fiber, or leather with padding/straps.
4. Functional Control
- CFO:
- Influences foot mechanics only.
- Controls motion at the subtalar joint and midfoot.
- Does not directly restrict ankle dorsiflexion/plantarflexion.
- AFO:
- Influences both foot and ankle mechanics.
- Can restrict or allow ankle motion depending on design (rigid vs hinged AFO).
- Provides significant stability and can substitute for weak muscles.
5. Shoe Requirements
- CFO:
- Fits inside most regular footwear (though depth/width may matter).
- Often interchangeable between shoes.
- AFO:
- Requires extra-depth or specialty shoes to accommodate brace bulk.
- Less interchangeable between shoe styles.
6. Level of Support
- CFO: Low to moderate support — mostly alignment and pressure relief.
- AFO: High support — stabilizes both foot and ankle, corrects deformity, assists or restricts motion.
In short:
- A CFO is best for controlling foot biomechanics inside a shoe.
- A custom AFO is prescribed when there is a need to control or support the ankle joint in addition to the foot—often for more severe deformity, weakness, or instability.
Custom Foot Orthotic vs Custom Ankle Foot Orthotic
|
Feature |
Custom Foot Orthotic (CFO) |
Custom Ankle Foot Orthotic (AFO) |
|
Primary Purpose |
Supports and aligns the foot only |
Supports and aligns the foot + ankle |
|
Conditions Treated |
Plantar fasciitis, metatarsalgia, flatfoot, high arches, overpronation, diabetic pressure relief |
Foot drop, ankle instability, severe PTTD, Charcot, neuromuscular disorders, post-stroke weakness, severe arthritis/deformity |
|
Structure |
Custom shoe insert (under the foot) |
Brace enclosing foot, extending above the ankle/lower leg |
|
Materials |
EVA, polypropylene, carbon fiber, multilayer composites |
Rigid plastics, carbon fiber, leather, padding, straps |
|
Functional Control |
Controls subtalar/midfoot motion; redistributes pressure |
Controls ankle + foot; can restrict or assist motion; provides major stability |
|
Shoe Requirements |
Fits most standard shoes (may need depth/width) |
Usually requires extra-depth or specialty shoes |
|
Level of Support |
Low–moderate (alignment, cushioning, offloading) |
High (stability, deformity control, motion assistance/restriction) |
|
Mobility Impact |
Subtle — improves gait efficiency through foot mechanics |
Major — can restore or substitute for lost muscle function, prevent falls, stabilize gait |
|
Best For |
Mild–moderate biomechanical or pressure issues |
Severe deformity, weakness, or instability involving both ankle and foot |
Summary:
- Use a CFO when the issue is mainly in the foot and can be managed inside the shoe.
- Use a custom AFO when the issue involves the ankle and foot together, especially when stability, motion control, or muscle substitution is required.






